What is DNA?
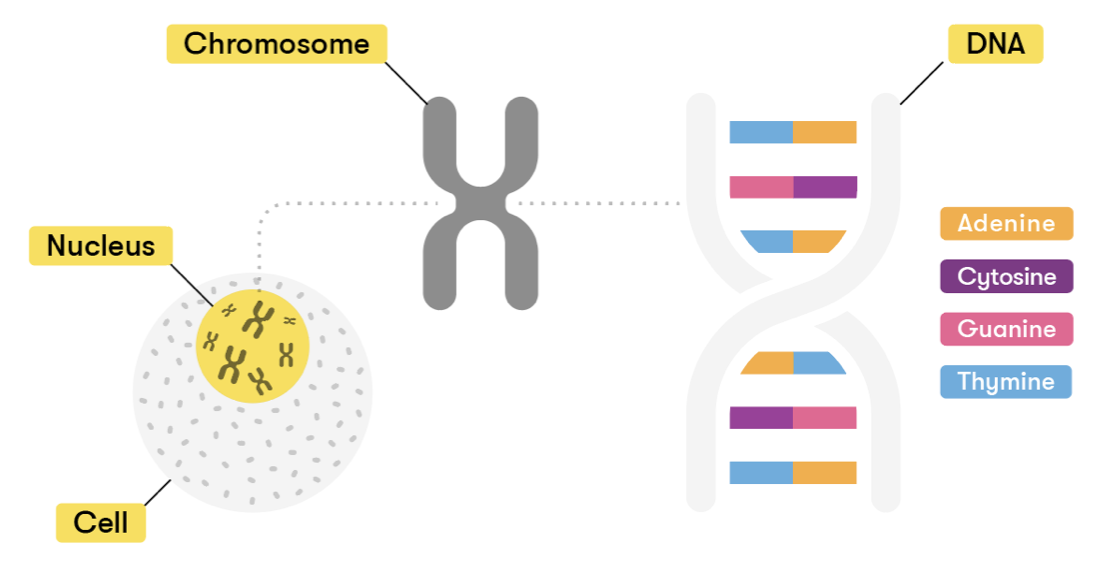
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a long complex molecule that holds all the information required for making proteins that help maintain an organism.
DNA is typically found in the nucleus of the cell, with some in the mitochondria. It has a double helix shape with two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked together by hydrogen bonding between base pairs.
DNA works like a computer. The cell is the computer and DNA is the programming code. The information in the DNA is stored as a code made up of four different bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). These bases, also known as nucleotides, are held together by hydrogen bonds between the two strands of the DNA. The adenine can only form a base pair with thymine whereas cytosine can only form a base pair with guanine. The sequence of these bases will determine different combinations for building and maintaining an organism. It is this sequence that gives instructions for the formation of our genes.
What is a gene?
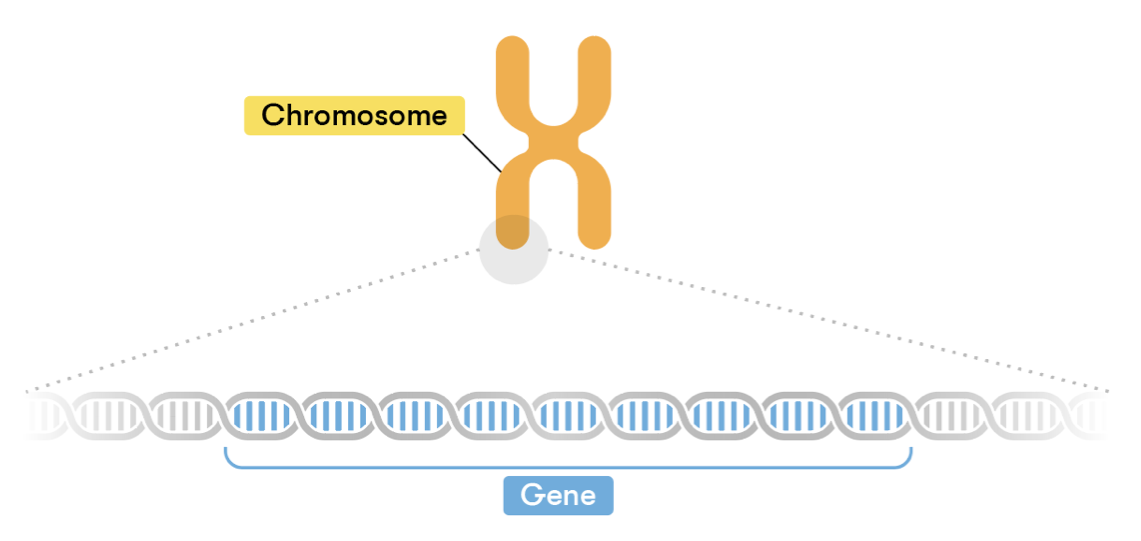
A gene is a segment of DNA that influences both the physical appearance and the internal functions of the body. They provide instructions to encode proteins to build and maintain an organism.
The human DNA contains about 20,000 genes on 23 pairs of chromosomes. Most people have the same genes, however; a small number of genes vary between individuals making them unique. This small difference is due to variations in the sequencing of DNA bases, which makes no body ordinary.
What is an rs number?
The ‘rs’ stands for the ID number used by databases and researchers to identify the location of a specific SNP.
What is an allele/genetic variant?
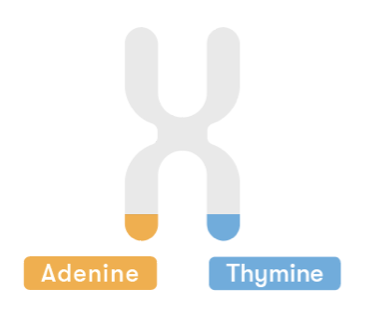
An allele refers to a variant form of a gene. Humans inherit two alleles (one from each parent) for each gene. The combination of these alleles represents an individual’s genotype.
An individual’s genetic makeup can be described as either homozygous or heterozygous. Homozygous refers to two identical alleles from a particular gene whereas heterozygous have two different alleles. The combination of carried alleles can contribute to an individual’s phenotype, which is the external trait of the organism.
Alleles are also classified as either dominant or recessive. If an individual carries one dominant allele and one recessive allele, it is likely the dominant phenotype that will be expressed in this individual. For example, you might carry one allele for brown eyes and one allele for blue eyes. Because brown eyes alleles are dominant you would express a brown eye colour. However, alleles may also attribute minor variations in the DNA sequence which does not affect an individual’s phenotype.
Difference between homozygous and heterozygous
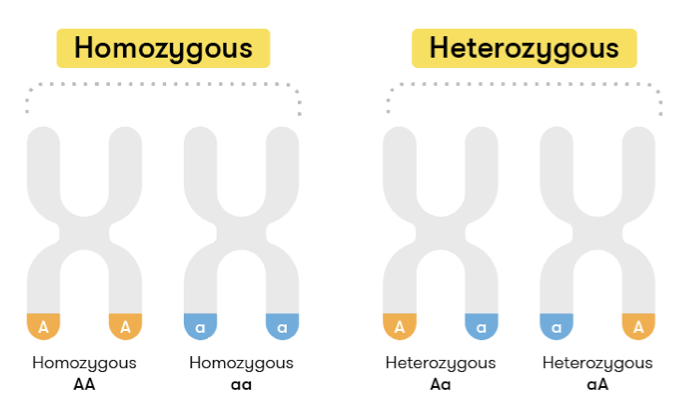
A person carrying two identical alleles of a specific gene is called homozygous whereas heterozygous refers to a person carrying different alleles of a specific gene.
For example, an individual carrying two identical alleles (A;A) of FTO rs9939609 polymorphism carry the same trait of a gene and it is classified as homozygous. If an individual carries different alleles (A;T) of the FTO rs9939609 polymorphism means this person carries different traits of a specific allele and is classified as heterozygous.
What is polymorphism?
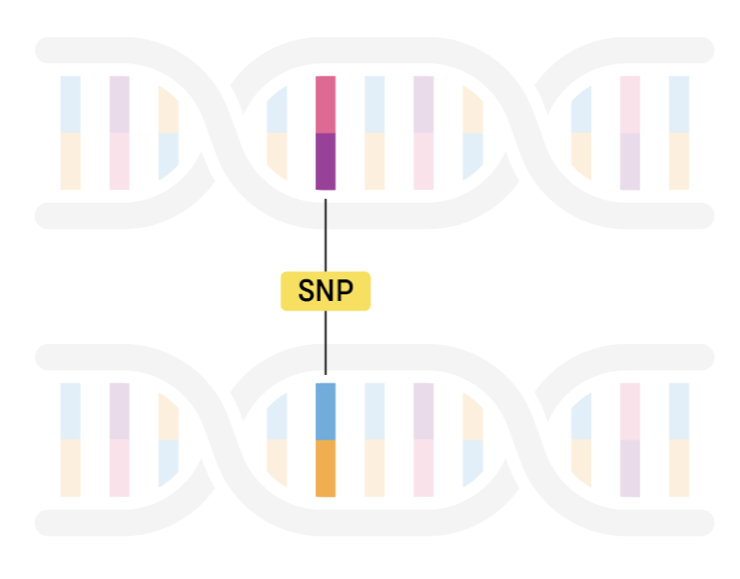
A genetic polymorphism refers to a particular DNA sequence that involves two or more alleles or discontinuous genotypes in a population.
Polymorphism refers to variations in the DNA sequence that occur with a frequency of ≥ 1% between individuals.These may affect individual phenotypes.
Most polymorphisms hold variations at a single base pair of the DNA. Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP, pronounced “snips”) refers to differences of nucleotides in a certain stretch of DNA. For example, the replacement of thymine (T) with the nucleotide cytosine (C).
Genetic predisposition or genetic susceptibility
Genetic predisposition refers to the susceptibility of an individual to develop a particular disease due to inherited genes. A genetic predisposition means a person carries at least one risk variant of a gene and it can influence an individual’s phenotype under environmental conditions.
Difference between genotype and phenotype
A genotype is the genetic makeup of an individual that is inherited from embryonic formation to adulthood. A human genotype refers to the entire genes inherited. This means humans carry one allele inherited from the mother and other from the father. This genetic combination constitutes an organism.
A phenotype refers to an individual’s physical and behavioral characteristics such as eye colour, height, shape, metabolic activities, and type of hair. Phenotypes are observable traits determined by the interaction of an individual’s genotype and environmental factors. The difference from genotype is that phenotype relies on an individual's traits without affecting the DNA, whereas genotype is the total genetic inheritance transmitted to the next generation.